Strahlentherapie des Glioblastoms
Allgemeines
Dosierung
GBM1 54 Gy, ED 1,8 Gy
Prognose
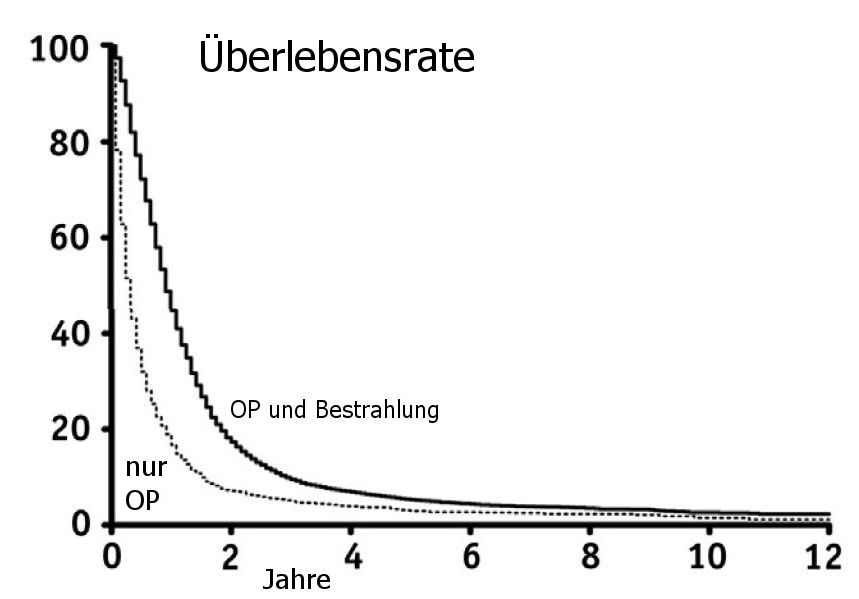
Modifiziert nach (1). SEER-analyse.
Zielvolumen (5)
PET
OAR
Quellen
The Impact of Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for High-Grade Gliomas by Histology in the United States Population.
Int J Radiation Oncol Biol Phys 2014;90:894-902. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.07.046
2.) Keime-Guibert F, Chinot O, Taillandier L, et al.:
Radiotherapy for glioblastoma in the elderly.
N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 1527-35.
3.) Laperriere N, Zuraw L, Cairncross G, Cancer Care Ontario:
Practice Guidelines Initiative Neuro-Oncology Disease Site Group.
Radiotherapy for newly diagnosed malignant gliomain adults: a systematic review.
Radiother Oncol 2002;64:259–73.
4.) Mason WP, et al. for the Canadian GBM Recommendations Committee:
Canadian recommendations for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme.
Curr Oncol 2007;14:110–117
5.) Niyazi M, et al.:
ESTRO-EANO guideline on target delineation and radiotherapy details for glioblastoma.
Radiotherapy and Oncology 2023;184: 109663
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2023.109663
6.) van den Bent MJ, Geurts M, French PJ, Smits M, Capper D, Bromberg JEC, et al.:
Primary brain tumours in adults.
Lancet 2023;402:1564 – 79.
7.) Galldiks N, Niyazi M, Grosu AL, Kocher M, Langen KJ, Law I, et al.:
Contribution of PET imaging to radiotherapy planning and monitoring in glioma patients - a report of the PET/RANO group.
Neuro-Oncology 2021;23:881 – 93.
8.) Albert NL, Weller M, Suchorska B, Galldiks N, Soffietti R, Kim MM, et al.:
Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology working group and European Association for Neuro-Oncology recommendations for the clinical use of PET imaging in gliomas.
Neuro-Oncology 2016;18:1199 – 208.
v
Teil von
