| zurück
Home |
DLBCL
Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
diffuses großzelliges B-Zell-Lymphom |
| allgemeines |
Früher Retikulosarkom |
Epidemiologie |
30-40% der hochmalignen Lymphome. BRD: 3000 Neuerkrankungen pro Jahr. Mortalität 25%. |
Klinik |
40% nur Lymphknotenbefall. |
40% haben extranodalen Befall:
- Gastrointestinaltrakt
- Haut
- Nervensystem
- Knochen
- Hoden
- Weichteile
- Speicheldrüsen
- weiblicher Genitaltrakt
- Lunge
- Niere
- Leber
|
Prognose |
Nach R-CHOP haben 35-40% ein Rezidiv oder sind Therapie-refraktär(2).
Salvage-autologe Stammzell-Transplantation: 60% nicht geeignet oder Rezidiv
nach ASCS(3) |
International Prognostic Index:
- > 60 Jahre
- ECOG > 1
- LDH erhöht
- Stadium III, IV
|
Diagnostik |
primärer Milzbefall
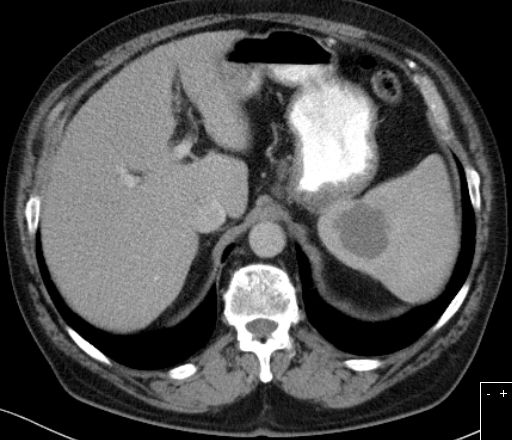 |
Pathologische subtrochantäre Fraktur bei extranodalem, intraossärem DLBCL.
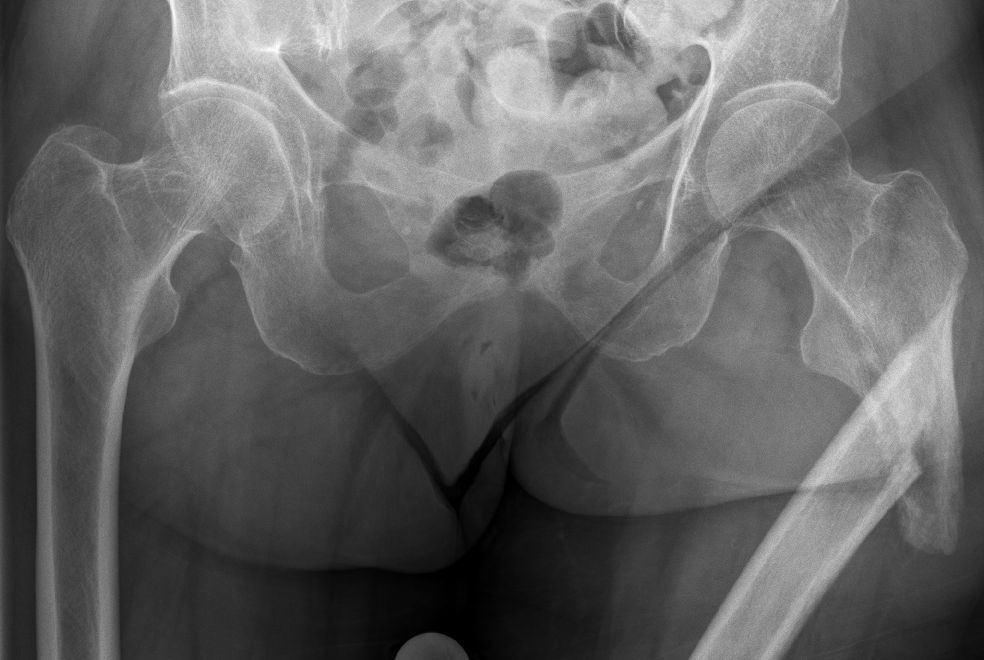 |
Morphologie |
Subtypen |
- PMBL (primary mediastinal B - cell lymphoma)
- GCB (germinal - center B - cell - lymphoma)
- ABC (activated B - cell - lymphoma)
|
primär mediastinales DLBCL, PMBCL |
Stammt von medullären Thymuszellen ab. |
mediastinaler Bulk, oft mit Infiltration von Lungen, Pleura, Pericard. |
BCR |
B-Cell-Receptor, ein chronisch activer BCR (ABC DLBCL) ist für das Überleben einer bösartigen Variante des DLBCL erforderlich. |
Beteiligt sind CARD11 und NF-κB. 10% der ABC DLBCLs haben Mutationen von CARD11 die NF-κB5 aktivieren. |
ABC - Subtyp |
activated B-cell–like subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Aggressive Variante des DLBCL. |
NF-κB Activierung durch permanente aktive B-Zell - Rezeptor (BCR) Signalbildung. Vermittelt wird dies durch Activität von PI3K und PDK1 (downstream kinase). |
PI3K -Inhibition reduziert die NF-κB Activität. PI3K und PDK1 sind notwendig für die MALT1 - Protease - Activität, einem Überlebensfaktor von ABC-DLBCL - Zellen (1). |
PB-DLBCL |
Primary Bone - DLBCL |
Therapie |
First-line-Therapie: R-CHOP (Rituximab, Cyclophosphamid, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, Prednisolone) |
Ergebnisse |
CRUKE/03/019: Testet R-CHOP-14 gegen R-CHOP-21. |
NHL-B2. RICOVER. |
SWOG-9704: autologe Stammzelltransplantation |
Radiatio |
Chemotherapie |
R-CHOP |
Target-Therapie | Enfortumab Vedotin, Padcev® |
Nectin-4-Antikörper konjugiert mit Monomethylauristatin E (Microtubulus-Inhibitor) |
In Kombination mit Rituximab, Cyclophosphamid, Doxorubicin, Prednisolon
First line Therapie
KV 2023: nicht quantifizierbar Zusatznutzen |
Teil von |
NHL, Non - Hodgkin - Lymphome |
Maligne Systemerkrankungen |
Onkologie |
Quellen |
1.) Kloo B, et al.:
Critical role of PI3K signaling for NF-κB–dependent survival in a subset of activated B-cell–like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells.
PNAS (2011) online: www.pnas.org, doi:10.1073/pnas.1008969108
Helmholz-Institut, München
2.) Sehn LH, Gascoyne RD:
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: optimizing outcome in the context of clinical and biologic heterogeneity.
Blood 2015;125:22-32
3.) Gisselbrecht C, Glass B, Mounier N, et al.:
Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era.
J Clin Oncol 2010;28:4184-90.
|

|

