| GTVp |
Primärtumor-Volumen |
|
| CTVp |
GTVp + 7 mm |
Primärtumor, clinical target volumen |
| PTVp |
CTVp + 5 mm |
Primärtumor, physical target volumen |
| GTVn |
befallene Lymphknoten |
|
| CTVn |
GTVn + 5 mm |
befallene Lymphknoten, clinical target volumen |
| PTVn |
CTVn + 5 mm |
befallene Lymphknoten, physical target volumen |
| HN3 |
PTVp + PTVn |
ca. 70 Gy, makroskopisch befallenes Gebiet |
| CTVhr |
Volumen mit hohem Risiko |
z,B. ipsilateral Level II,III,IV |
| PTVhr |
CTVhr + 5 mm |
|
| HN2 |
HN3 + PTVhr |
ca. 59 Gy |
| CTVlr |
Volumen mit niedrigem Risiko |
z.B. kontalateral Level II, III, IV |
| PTVlr |
CTVlr + 5 mm |
|
| HN1 |
HN2 + PTVlr |
z.B. 50Gy |
|
| GTVp |
Primärtumor-Volumen |
|
| CTVp |
GTVp + 7 mm |
Primärtumor, clinical target volumen |
| PTVp |
CTVp + 5 mm |
Primärtumor, physical target volumen |
| GTVn |
befallene Lymphknoten |
|
| CTVn |
GTVn + 5 mm |
befallene Lymphknoten, clinical target volumen |
| PTVn |
CTVn + 5 mm |
befallene Lymphknoten, physical target volumen |
| HN3 |
PTVp + PTVn |
ca. 70 Gy, makroskopisch befallenes Gebiet |
| CTVhr |
Volumen mit hohem Risiko |
z,B. ipsilateral Level II,III,IV |
| PTVhr |
CTVhr + 5 mm |
|
|
| GTVp |
Primärtumor-Volumen |
|
| CTVp |
GTVp + 7 mm |
Primärtumor, clinical target volumen |
| PTVp |
CTVp + 5 mm |
Primärtumor, physical target volumen |
| GTVn |
befallene Lymphknoten |
|
| CTVn |
GTVn + 5 mm |
befallene Lymphknoten, clinical target volumen |
| PTVn |
CTVn + 5 mm |
befallene Lymphknoten, physical target volumen |
| HN3 |
PTVp + PTVn |
ca. 70 Gy, makroskopisch befallenes Gebiet |
| CTVhr |
Volumen mit hohem Risiko |
z,B. ipsilateral Level II,III,IV |
| PTVhr |
CTVhr + 5 mm |
|
| HN2 |
HN3 + PTVhr |
ca. 59 Gy |
| CTVlr |
Volumen mit niedrigem Risiko |
z.B. kontalateral Level II, III, IV |
| PTVlr |
CTVlr + 5 mm |
|
| HN1 |
HN2 + PTVlr |
z.B. 50Gy |
|
3-Feldertechnik |
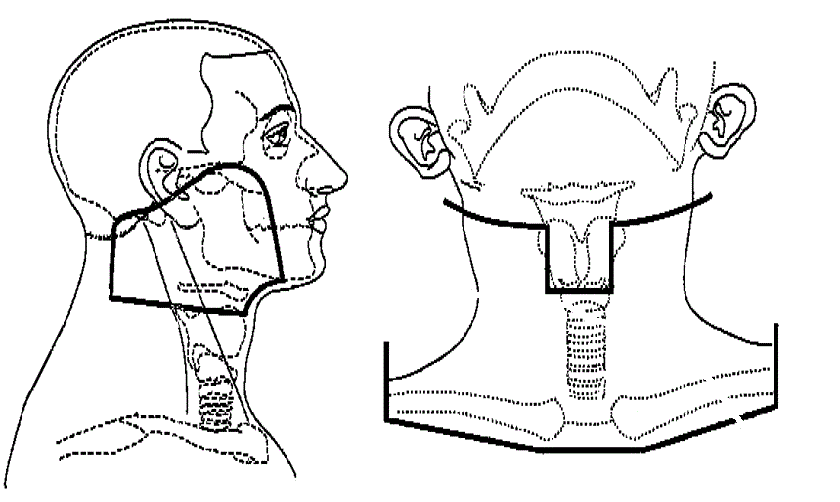 volumen volumen
Diese 3-Feldertechnik wurde bis vor wenigen Jahren eingesetzt. Heute obsolet!
Die Parotis ist beiderseits zu 100% erfasst. |
| Fraktionierung |
MARCH: Meta-Analysis of Radiotherapy in Carcinomas of Head and neck Collaborative Group.
|
| Mukositis |
Dische Scoringsystem für akute Mukositis
| Kriterium |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| Mucosal reactions |
none |
slight erythema |
marked erythema |
spotted mucositis |
confluent mucositis |
| Area involved | none |
=25% |
25– 50% |
50–100% |
| Edema |
none |
slight |
moderate |
severe |
| Bleeding | none |
slight incidental |
slight, multifocal |
marked, regular |
| Ulceration | none |
single, superficial |
multifocal, superficial |
single, profound |
multifocal, profound |
| Dysphagia (diet) |
normal |
exclusion of some food |
soft, pulp food only |
fluids only |
tube feeding or intravenous alimentation |
| Pain | none |
during eating only |
constant, but moderate, non-steroidal analgesics |
constant, serious, narcotics needed |
|
| Xerostomie |
Durch Gabe von 25mg Bethachenol kann die akute
Xerostomie verringert werden(2). |
| Schilddrüse |
Die Bestrahlung von HNO - Tumoren führt
gelegentlich zu einer Hypothyreose(1). |
| LK-Level |
RTOG - Definition
| LEVEL |
CRANIAL |
CAUDAL |
ANTERIOR |
POSTERIOR |
LATERAL |
MEDIAL |
| Ia |
Geniohyoid m., plane tangent to basilar edge of mandible |
Plane tangent to body of hyoid bone |
Symphysis menti, platysma m. |
Body of hyoid bone |
Medial edge of ant. belly of digastric m. |
n.a.a |
| Ib |
Mylohyoid m., cranial edge of submandibular gland |
Plane through central part of hyoid bone |
Symphysis menti, platysma m. |
Posterior edge of submandibular gland |
Basilar edge / innerside of mandible, platysma m., skin |
Lateral edge of ant. belly of digastric m. |
| IIa |
Caudal edge of lateral process of C1 |
Caudal edge of the body of hyoid bone |
Post. edge of submandibular gland; ant. edge of int. carotid artery; post. edge of post.
belly of digastric m. |
Post. Border of int. jugular vein |
Medial edge of sternocleidomastoid |
Medial edge of int. carotid artery, paraspinal (levator scapulae) m. |
| IIb |
Caudal edge of lateral process of C1 |
Caudal edge of the body of hyoid bone |
Post. Border of int. jugular vein |
Post. border of the sternocleidomastoid m. |
Medial edge of sternocleidomastoid |
Medial edge of int. carotid artery, paraspinal (levator scapulae) m. |
| III | Caudal edge of the body of hyoid
bone |
Caudal edge of cricoid cartilage |
Postero-lateral edge of the sternohyoid m.; ant. edge of sternocleidomastoid
m. |
Post. edge of the sternocleidomastoid m. |
Medial edge of sternocleidomastoid |
Int. edge of carotid
artery, paraspinal (scalenius) m. |
| IV |
Caudal edge of cricoid cartilage |
2 cm cranial to sternoclavicular joint |
Anteromedial edge of sternocleido-mastoid m |
Post. edge of the sternocleidomastoid m. |
Medial edge of sternocleidomastoid |
Medial edge of internal carotid
artery, paraspinal (scalenius) m. |
| V |
Cranial edge of body of hyoid bone |
CT slice encompassing the transverse cervical vesselsb |
Post. edge of the sternocleidomastoid m. |
Ant. border of the trapezius m. |
Platysma m., skin |
Paraspinal (levator scapulae, splenius capitis) m. |
| VI |
Caudal edge of body of thyroid cartilagec |
Sternal manubrium |
Skin; platysma m. |
Separation between trachea and esophagus |
Medial edges of thyroid gland, skin and
ant.-medial edge of sternocleidomastoid m. |
n.a. |
| Retro- pharyngeal |
Base of skull |
Cranial edge of the body of hyoid bone |
Fascia under the pharyngeal mucosa |
Prevertebral m. (longus colli, longus capitis) |
Medial edge of the internal carotid artery |
Midline |
|
| Kosten USA (5) |
Analyse der Zahlungen von Medicare (USA)aus dem Jahr 2016
- Radikaloperation ~$18,000
- Bestrahlung nach konventioneller 3-D Planung ~$32,000
- IMRT ~$95,000.
|
| Quellen |
1.) Turner SL, Tiver KW, Boyages SC:
Thyroid dysfunction following radiotherapy for head and neck cancer.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1995;31:279-83
2.) Jaguar GC, et al.:
Double blind randomized prospective trial of bethanechol in the prevention of
radiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction in head and neck cancer patients.
Radiotherapy and Oncology 2015;115:253–256
3.) Mazeron JJ, Ardiet JM, Haie-Meder C, et al.:
GEC-ESTRO recommendations for brachytherapy for head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas.
Radiother Oncol 2009;91:150-156
4.) Garden AS, Beadle BM, Gunn BG:
Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancers: Indications and Techniques.
5th Edition Wolters & Cluver 2017
5.) Razfar A, Mundi J, Grogan T, et al.:
IMRT for head and neck cancer: Cost implications.
Am J Otolaryngol. 2016;37(6):479-483.
doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2015.02.017.
6.) Yong JHE, et al.:
Estimating the costs of intensity-modulated and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in Ontario.
Curr Oncol 2016;23:e228-e238
|
| wichtiger Hinweis! |
Für die Richtigkeit von Dosisangaben, Zielvolumina
und Indikationen kann keine Garantie übernommen werden. In Zweifelsfällen sind
die aktuellen nationalen und internationalen Leitlinien einzusehen. |

|
|
Impressum
Zuletzt geändert am
20.12.2015 11:54
|
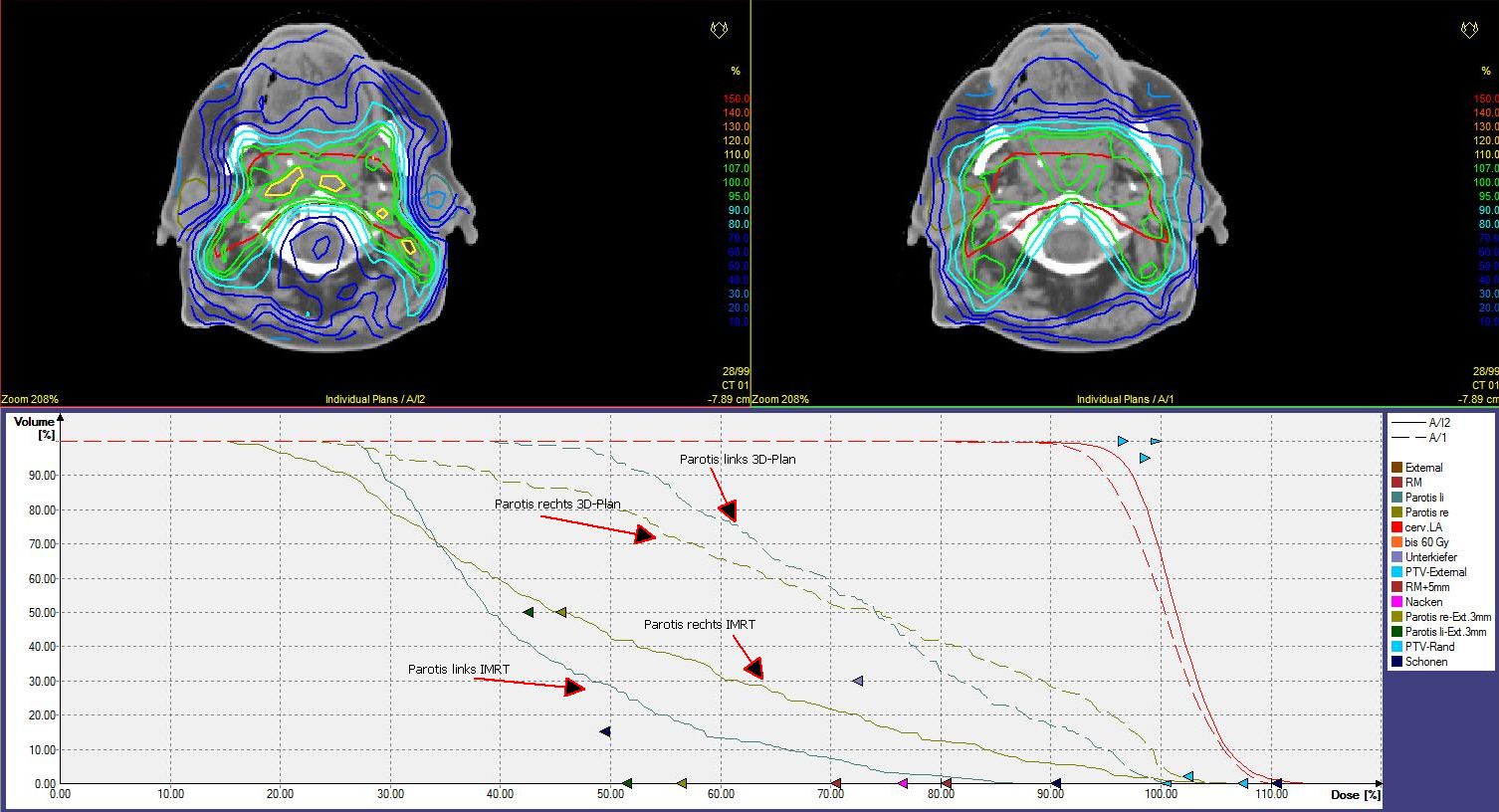
 volumen
volumen