atypische duktale Hyperplasie (ADH) oder atypische lobuläre Hyperplasie (ALH)
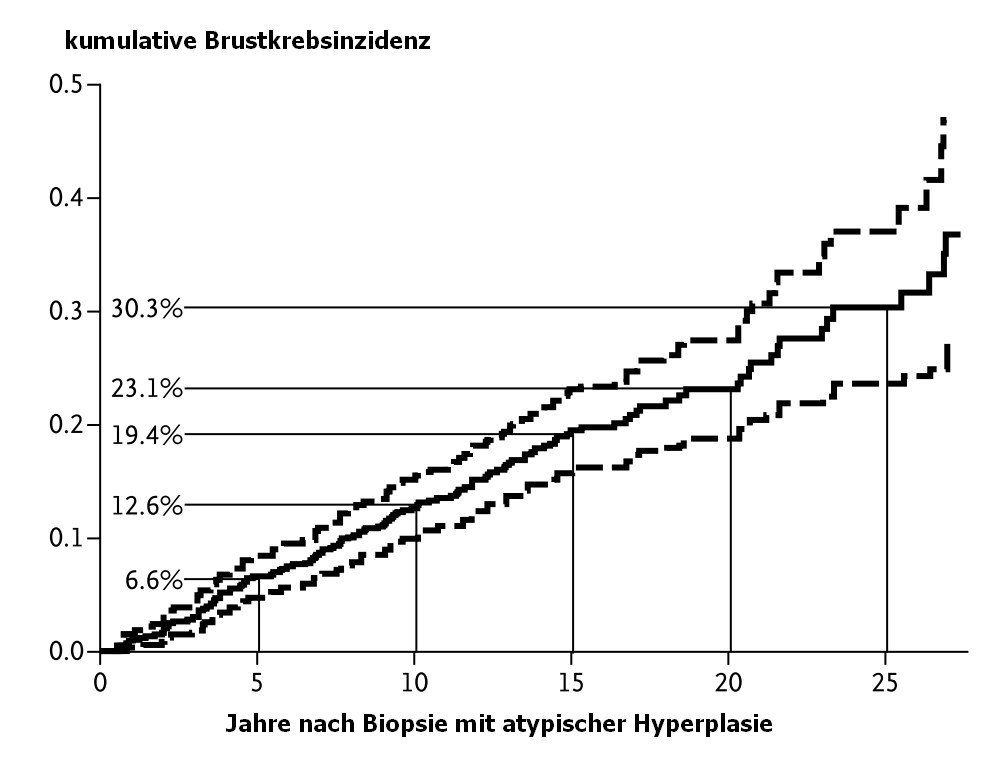
Die gestrichelte Linien kennzeichnen den 95%-Vertrauensbereich. Nach Zahlen der Majo-Klinik (2)
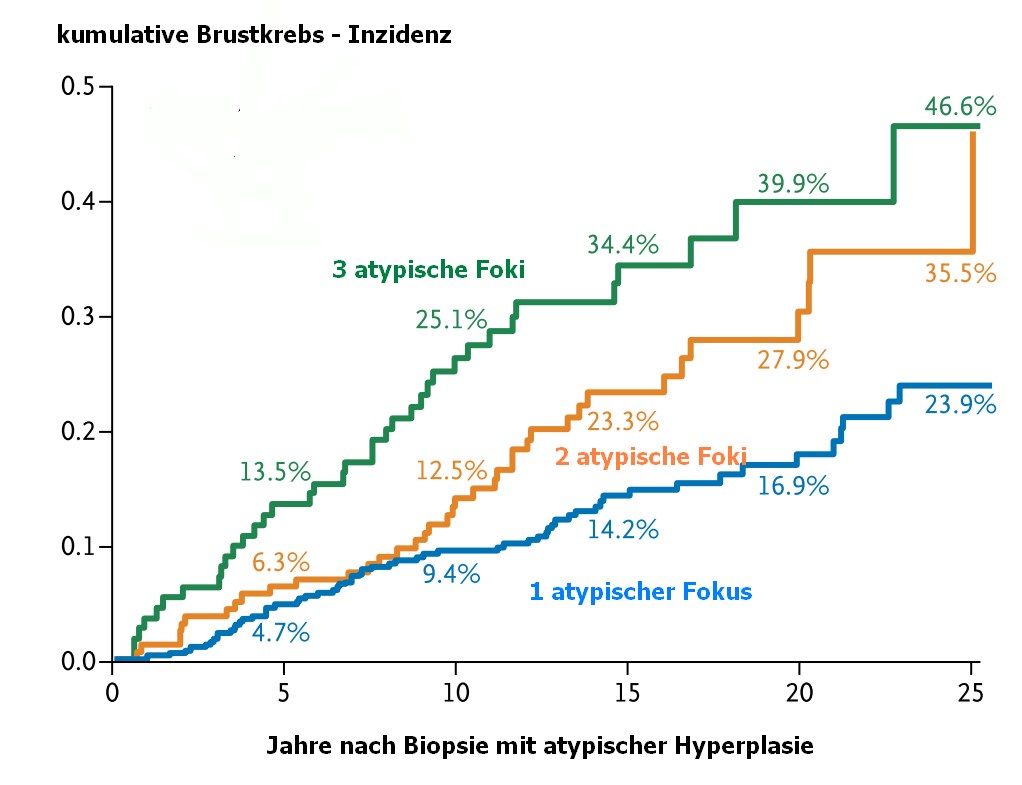 Nach Zahlen der Majo-Klinik (2)
Nach Zahlen der Majo-Klinik (2)nach Exzision 3,0
- 5,7 % binnen 10 Jahren an invasivem Brustkrebs.
- Nach Nadelbiopsie 5 %
- nach Exzision 6,7 %.
- LCis: lobuläres Carcinoma in situ
- PLCis:pleomorphes lobuläres Carcinoma in situ
- ALH: atypische lobuläre Hyperplasie
einfache duktale Hyperplasie, Zylinderzellhyperplasie, FEA, ADH, DCIS,
Teil von
Combined histologic and cytologic criteria for the diagnosis of mammary atypical ductal hyperplasia.
Hum Pathol 1992;10:1095-1097.
2.) Hartmann LC:
Atypical Hyperplasia of the Breast — Risk Assessment and Management Options.
NEJM 2015; 372: 78-89
DOI: 10.1056/NEJMsr1407164
3.) Hartmann LC, Radisky DC, Frost MH, et al.:
Understanding the premalignant potential of atypical hyperplasia through its natural history: a longitudinal cohort study.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2014;7:211-7.
4.) Page DL, Schuyler PA, Dupont WD, Jensen RA, Plummer WD , Simpson JF:
Atypical lobular hyperplasia as a unilateral predictor of breast cancer risk: a retrospective cohort study.
Lancet 2003;361:125-9
5.)Menes TS, et al.:
Subsequent breast cancer risk following diagnosis of atypical ductal hyperplasia on needle biopsy.
JAMA Oncol 2017; 3: 36–41.
